Riccia thallus structure and reproduction
- 1. RICCIA Prepared by: Dr. E. Gayathiri Department of Plant Biology and Plant Biotechnology Guru Nanak College, Chennai
- 2. OVERVIEW • HABITAT • EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THALLUS • REPRODUCTION IN THALLUS • ALTERNATION OF GENERATION
- 3. Classification (Systematic position) • Kingdom: Plantae • Subking.: Cryptogams • Division : Bryophyta • Class : Hepaticopsida • Order : Marchantiales • Family : Ricciaceae
- 4. Habitat • 1. The genus Riccia comprises about 138 species. 2. 33 species have been recorded so far R. crystallina, R. kashyapii, R. pandel are endemic in India. 3. Riccia mainly grows on damp soil and shady places and other similar terrestrial habitats.
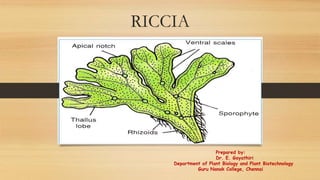
- 5. External Structure of Thallus 1. Due to dichotomous branching a circular patch of plants is formed which is called rosette. 2. Plant body represents haploid, the gametophyte generation. R. fluitans, the aquatic species, is partially submerged or it floats in water.
- 6. Riccia thallus-Rhizoid • Rhizoids are unicellular and unbranched. • Two types of rhizoids, - smooth walled and tuberculated. • Rhizoids - fixation and absorption. • The scales in young plants are arranged in one transverse row near the apex. • When the thallus matures, they form two rows near the margin of the thallus. Source: http://selfstudy.co/sp/medical/botany/plant-kingdom/bryophyta/5acd971ba0a9b5775fdb62be
- 7. Internal structure of thallus A vertical section of thallus has depression in the centre - dorsal groove. Internal differentiation. The thallus is formed of two distinct regions, viz. a. the lower or ventral storage region and b. an upper or dorsal photosynthetic or assimilatory region Source: http://premabotany.blogspot.com/2018/12/riccia-classification-structure-of.html
- 8. Storage region In the ventral surface - closely packed parenchymatous tissue are present The chloroplasts are absent in this region. The region acts as storage tissue, storing water and reserved food material (starch). From the lower epidermal cells, develop rhizoids and amphigastria. The rhizoids help in absorption while the amphigastria give protection. Source: http://premabotany.blogspot.com/2018/12/riccia-classification-structure-of.html
- 9. Photosynthetic region Present on the dorsal surface It consists of chlorenchymatous cells with one cell thickness. These vertical rows of cells are called photosynthetic filaments. Between the chlorenchymatous rows - air chambers, air-canals are air-clefts. The air chamber lacks photosynthetic filaments. Around the air cleft six to eight vertical rows of chlorenchymatous cells, terminal bigger colorless cell Source: http://premabotany.blogspot.com/2018/12/riccia-classification-structure-of.html
- 10. Photosynthetic region Terminal cells together form an interrupted upper epidermis. The air-cleft communicate with the outer environment through the gaps called air-pores. In the case of the aquatic species, the epidermis is continuous and air-pores are absent. The thallus shows large air-cavities which store air and give buoyancy to the plant. The epidermal cells also show presence of chloroplasts.
- 11. Reproduction A.Vegetative B.Sexual 1. Fragmentation 2. Adventitious branches 3. Tubers 4. Persistent apices
- 12. Reproduction A. Vegetative 1. Fragmentation –Older cell on decay the older dichotomy separate - favourable conditions, - new thallus. 2. Adventitious branches – arise from the mid-ventral surface of the thallus - detached - new plants. Source: http://Slideplayer
- 13. Reproduction A. Vegetative 1. Tubers - The tips of branches store food material and become swollen - tubers. In favourable - new plants. 2. Persistent apices – prolonged dry conditions, the plant dies except the apical part. This apical part however grows deep into soil and becomes thick. It resumes active growth in next season and develops into a new thallus. Source: http://premabotany.blogspot.com/2018/12/riccia-classification-structure-of.html
- 14. Reproduction– B. Sexual:Oogamous type. The sex organs are well developed, multicellular and separate. The male reproductive organ - Antheridium (gametes, antherozoid). The female reproductive- Archegonium (gamete ,ovum) Both the sex organs - on the same plant- monoecious. on different plants- dioecious or unisexual. The sex organs are in the dorsal surface ,deeply sunk in the mid-furrow of the thallus. Source: http://Madanacademy, Self study.co
- 15. Antheridium : • multicellular and elongated structure enclosed in an antheridial cavity consists of a stalk and a body body is ovoid or pear-shaped outermost sterile layer called the jacket layer or the antheridial wall - protective encloses a mass of fertile, cubical cells called androcyte mother cells Each mother cell divides to form two androcytes or spermatids numerous antherozoids or spermatozoids are formed in an antheridium.
- 16. Antherozoid : spermatozoid is a minute, slender, curved and flagellate structure. Flagella are two in number The body possesses elongated blepharoplast, a nucleus and a little cytoplasm. The unused cytoplasm remains attached to the posterior end forming a vesicle.
- 17. Archegonium Present in a cavity (Archegonial cavity). Archegonium is flask shaped. Archegonium formed of three parts - stalk, ventre and neck Stalk is small and few celled Archegonium
- 18. Archegonium Venter is broad & venter wall is one cell in thickness Venter encloses a cavity - venter cavity two unequal cells smaller - ventral canal cell larger, posterior cell - ovum or the egg cell Neck consists of six vertical rows of cells At the tip - four specialized cells - lid cells or cover cells.
- 19. Dehiscence of Sex organs water or even moisture is necessary spermatozoids lie in the antheridial cavity because the walls of spermatids are already dissolved water finds its way to the antheridial cavity through the ostiole of the cavity antheridium bursts liberating antherozoids due to pressure created archegonium reaches maturity, the ventral canal cell and the neck canal cells disintegrate or degenerate to form mucilage mucilage absorbs more water and pressure is created separating the lid cells Sperms reach to the egg cell.
- 20. Fertilization: Certain chemical substances are exuded along with the mucilage These chemicals probably attract the spermatozoids. Only one of the antherozoids surrounding the egg succeeds in uniting with the egg Gametophytic stage ends with the process of fertilization. The zygote, the first cell of the sporophytic generation is embedded in venter
- 21. Sporophyte Zygote is the first cell of diploid or sporophytic generation The mature sporophyte of Riccia is the simplest among the sporophytes It consists of only capsule or the spore sac, while foot and seta are absent
- 22. Sporophyte The sporophyte is embedded in the storage tissue of the gametophyte and enclosed in the venter cavity of the archegonium. zygote divides mitotically to form sporogonium The sporophytes are last cells of diploid generation The sporophytes divide meiotically to produce haploid cells-spores
- 23. Sporophyte sporophyte is completely dependent for nutrition on the gametophyte - complete sporogonium of Riccia never dehisces surrounding calyptra decay or disintegrate, the spores remain behind on the soil. favourable conditions, they germinate to from new plants
- 24. Spores spore is tetrahedral spore wall or sporoderm is formed of two layers, the outer exine (exosporium), and the inner intine (endosporium) exine is variously ornamented exine is cuticularised, while the intine is thin walled
- 25. Spore germination presence of light and the presence of moisture spore absorbs water and the pressure created ruptures the exine. intine comes out forming a short germ tube contents of the spore migrate to the tip of the germ-tube and a partition is formed division and redivision of the apical region results into a new gametophyte
- 27. Thank you
